NDT (Non-Destructive Testing)
NDT (Non-Destructive Testing) services refer to a range of techniques and methods used to inspect, evaluate, and analyze materials, components, and structures without causing any damage or alteration.
Overview
Certainly, NDT (Non-Destructive Testing) services refer to a range of techniques and methods used to inspect, evaluate, and analyze materials, components, and structures without causing any damage or alteration. These services are crucial in various industries to ensure the safety, quality, and integrity of assets. Here are some of the key NDT services provided by Belmont NDT UK and Belmont Asia.
The applications of NDT services are widespread and diverse. In the aerospace industry, NDT is employed to scrutinize aircraft components for hidden defects, while the automotive sector relies on these techniques to assess the quality of welds, castings, and other critical parts. In the energy sector, NDT is vital for inspecting pipelines, pressure vessels, and power plant components to prevent leaks and ensure uninterrupted energy supply. The construction industry utilizes NDT to assess the structural integrity of buildings and bridges, and the oil and gas sector relies on NDT to examine drilling equipment and storage tanks for safety and regulatory compliance.

Detects surface and near-surface flaws in ferromagnetic materials by applying a magnetic field and iron particles, commonly used in industries like aerospace and automotive.
Detects thermal anomalies and insulation defects by capturing temperature variations, commonly used in electrical and mechanical equipment maintenance.
A fundamental NDT method involving a thorough visual examination of materials and structures, typically used for initial assessments and as a complement to other NDT techniques.
Involves the use of X-rays or gamma rays to inspect the internal structure of objects, ideal for identifying flaws in welds, castings, and pipelines.
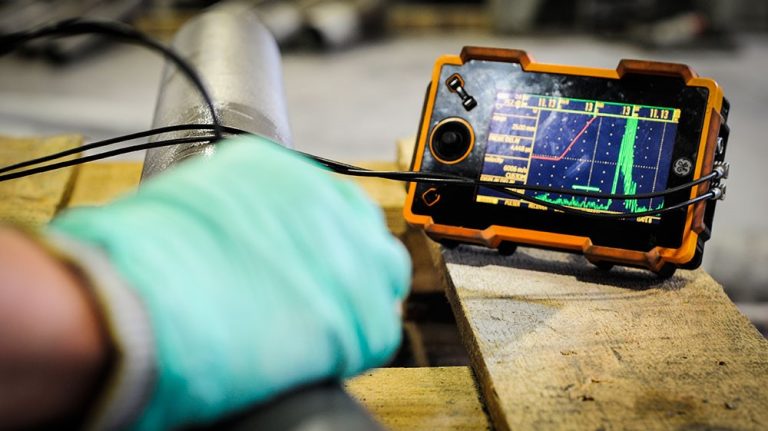
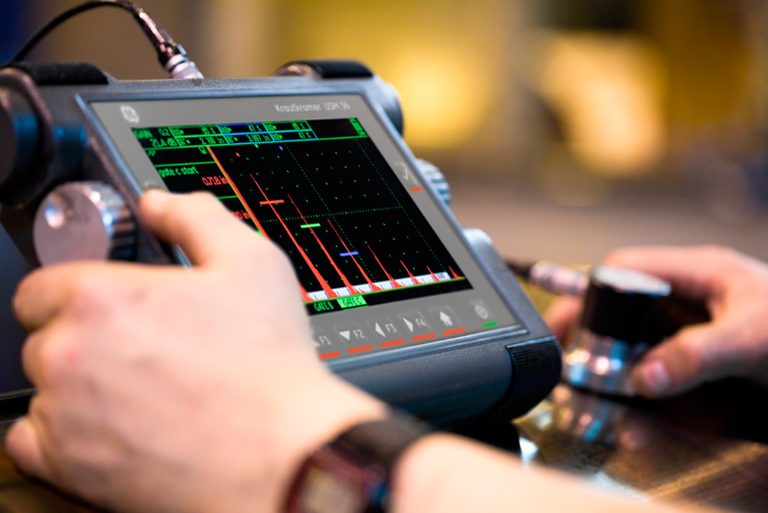
Utilizes high-frequency sound waves to detect defects or irregularities within materials, commonly used for weld inspection and thickness measurements.
Utilizes electromagnetic induction to identify defects in conductive materials, particularly useful for detecting cracks and corrosion in non-ferrous materials.
A method for finding surface cracks and defects by applying a penetrant and a developer to highlight imperfections, often used in the inspection of metals, plastics, and ceramics.
Involves the use of X-rays or gamma rays to inspect the internal structure of objects, ideal for identifying flaws in welds, castings, and pipelines